LED Lighting Power Supplies
Wall Industries, Inc. offers LED lighting solutions that withstand harsh environments and can be utilized in industrial or commercial lighting applications.
We offer encapsulated, open frame, and LED driver modules to provide reliable and efficient power to your LED lighting systems. Our solutions are designed with high efficiency and low power consumption in mind, and meet the highest safety standards required for lighting applications.
Whether you’re working on commercial, residential, or industrial LED lighting projects, our selection of LED lighting power supplies has you covered. Browse our collection to find the right supply for your application.
| Series | Input Range |
Input Voltage |
Output Voltage |
No. Outputs |
Output Power (W) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PSLRB6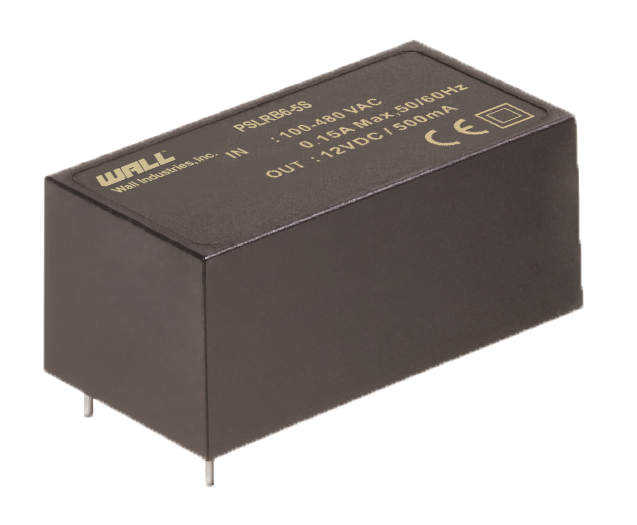 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 85~530 | Input Voltage: 100/480 | Output Voltage: 5, 12, 15, 24 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 6 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The PSLRB6 series of AC/DC power supplies offers up to 6 watts of output power in a compact 2.07” x 1.08” x 0.91” through hole package. | ||||||
PSHL20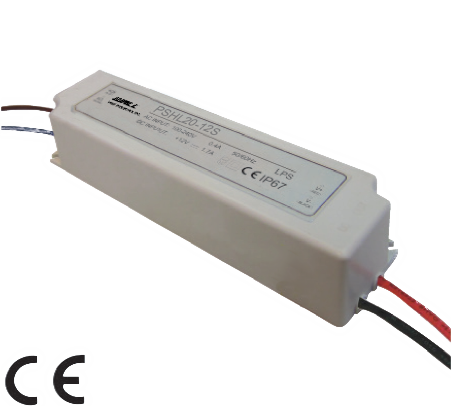 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 90~264 | Input Voltage: 115/230 | Output Voltage: 12, 24, 36, 48 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 20 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The PSHL20 series of LED drivers offers 20 watts of output power in a 5.83in x 1.57in x 1.18in package with plastic cover. | ||||||
PSHL55 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 176~265 | Input Voltage: - | Output Voltage: 18~35, 12~24, 24~48 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 55 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The PSHL55 series of LED drivers offers 55 watts of output power in a 6.42” x 1.79” x 1.24” package with plastic cover. | ||||||
LEDA100 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 120~277 | Input Voltage: 240 | Output Voltage: 12, 24 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 96 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The LEDA100 series of LED drivers offers 96 watts of output power in a 9.50” x 1.70” x 1.15” IP20 designed package. | ||||||
PSLHE100 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 120~277 | Input Voltage: 240 | Output Voltage: 12, 15, 24, 36 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 100 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The PSLHE100 series of constant voltage LED drivers offers up to 100 watts of output power in a 9.65” x 1.90” x 1.50” package. | ||||||
PSLHE150 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 120~277 | Input Voltage: 240 | Output Voltage: 12, 15, 18, 24, 30, 36, 48 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 150 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The PSLHE150 series of constant voltage LED drivers offers up to 150 watts of output power in an 8.98” x 2.68” x 1.52” package. | ||||||
PSMDC185 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 90~305 | Input Voltage: 115/230 | Output Voltage: 25~35, 27~42, 32~49, 29~58, 71~143, 95~190, 143~286, 200~400 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 177, 183, 189, 200 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The PSMDC185 series of LED drivers offers 183~200 watts of output power in an 8.62” x 2.64” x 1.57” aluminum package. | ||||||
PSLEDR400 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 120~277 | Input Voltage: 240 | Output Voltage: 24, 48 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 400 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The PSLEDR400 series of constant voltage LED drivers offers 400 watts of power in an 11.47” x 4.43” x 1.91” package. | ||||||
What is an LED power supply?
LED lighting power supplies (also known as LED drivers) provide LEDs with the power they need to function at their best and sustain performance over long periods of time. LEDs are notable for their light quality energy-saving qualities and long life spans, however, these are only attainable when powered using the appropriate LED power source.
LEDs save energy by running on direct current at lower voltages, compared to other lighting which runs on higher voltage alternating current. An LED power supply safely converts these higher alternating current voltages into the lower direct current voltages and appropriate currents that these lights need to perform correctly.
LED drivers protect LEDs from current fluctuations. Each LED light’s output is proportional to its current supply, so a change in voltage causes a change in light output. LEDs can quickly degrade or vary in performance if they are subjected to too much or too little current. LED drivers ensure that a consistent level of current is delivered to the lights, so performance can remain consistent and efficiency is retained.
How to choose an LED power supply
Choosing an LED power supply requires knowledge of your power source, the LEDs that you’re powering, as well as the conditions that they’ll be operating in, and where and how it will be installed.
Wattage
Find out how many watts your LED light will consume, if you’re planning on powering multiple lights with one power supply then you will need to sum the wattages in order to calculate the total watts they will use. Your LED power supply will need to be large enough to exceed this overall wattage. Typically, it’s recommended to buy a power supply that exceeds the wattage required by at least 20%, so that you can guarantee consistent performance.
Voltage/Current
Make sure to note the required input voltage of the LEDs that you are supplying power to as this will dictate the type of LED power supply that you will choose. LEDs requiring a fixed output current will require constant-current drivers. On the other hand, LEDs that require a fixed output voltage will need to be powered by constant-voltage drivers.
You’ll also need to confirm the line voltage that you will be working with, this varies depending on what country you are operating in. LED power supplies can be designed for low-line AC power, high-line AC power or a full range of AC power.
Using Dimmable LEDs?
If you’re using dimmable LEDs then you’ll need a power supply with dimming capabilities. Dimmable LED power supplies typically use one of two control types: pulse-width modulation dimming (PWM dimming), or TRIAC dimming (Triode for alternating current).
- PWM dimmers pulse lights at high frequencies to change our perception of light. These dimmers are usually built into LED strip lights functioning on the 12VDC side of the circuit. Wall-mounted or remote PWM dimmers can be used on all power supplies if needed.
- TRIAC dimming can only be used when power supplies qualify for alternating current (TRIAC) dimming – check the specifications of your power supply. TRIAC dimming power supplies create a change in power on the AC input side, which therefore varies the DC output, which then controls the brightness of your LEDs.
Operating Temperature
Your operating conditions will also determine the type of LED power supply that you choose. Power supplies have safe operating temperatures that should be adhered to in order to provide optimal performance and to prevent overheating. Consider the space that you are installing the power supply and ensure that you allow for appropriate ventilation of the unit.
Weather Conditions
Consider the weather conditions that your LED power supply will be operating in and choose your unit accordingly. Power supplies have IP (ingress protection) ratings that describe the degree to which the unit can resist the size of solids and pressure of liquids. This allows you to match your power supply’s resistance with the worst-case conditions that it could be operating in. For example, an IP67 rating is given to a unit that provides limited protection against dust and can be immersed between 15cm and 1m underwater.
Size & Shape
On a practical note, you’ll need to ensure that the LED power supply you choose is the right size and shape for your needs. If you are buying a replacement power supply then you’ll want to ensure that the unit fits in the space you have with enough space for ventilation to prevent over-heating.
Efficiency
The efficiency percentage of a power supply indicates the amount of power that is actually being used to light your LEDs. The higher this number, the more power you’ll be saving, so it makes sense to choose an LED power supply with an efficiency percentage of at least 80%.
Safety Approvals
There are a number of different safety approvals and classes that are used to differentiate power supplies. UL Class 2 drivers will comply with standard UL1310, which means that no major safety protection is required at the LED level and there is no risk of fire or electric shock. These drivers are limited at different voltages depending on their operating conditions, as such there are restrictions on how many LEDs Class 2 drivers can operate.
UL Class 1 drivers have high-voltage outputs and require additional safety protection; however, they can also operate more LEDs, making them more efficient than their UL Class 2 counterparts when a larger number of LEDs need to be powered.
What are constant voltage power supplies?
Constant voltage power supplies are used to convert AC to DC to store-bought LEDs, which usually have drivers or resistors built into them. 12V LED power supplies (or LED power adapters) take the standard household voltage of 120VAC down to the 12VDC that domestic 12V LEDs require.
Commercial LEDs will usually require a separate constant current driver or current limiting resistor in order to regulate current, ensuring that they stay at appropriate temperatures, maintain consistent performance and maximize their overall lifespan.
How do LED power supplies work?
LED power supplies work by converting incoming line power at various voltages to regulate DC output current at either a fixed or variable output. This output must be within a specific range in order to power an LED array without any flickering. LED drivers can be designed to accept a range of power sources, including Power over Ethernet (PoE) and DC power from DC micro-grids.
What is the difference between LED driver and power supply?
The term ‘LED drivers’ is used to refer to LED power sources that provide constant-current output. Historically, ‘LED power supplies’ were used to describe power supplies that provide constant-voltage to LEDs. These terms are used interchangeably today, however, it’s important to note whether the output voltage gives a ‘constant voltage’ or constant-current’ when making your choice of LED power supply.
How to troubleshoot LED power supply?
Before you repair your LED power supply, it’s important to determine the underlying issues behind its failure.
- Check that the specifications of your power supply are suitable for your LED lights.
- Ensure that your power supply has been correctly mounted. Each power supply has its own set of mounting restrictions, incorrect mounting can lead to overheating.
- Similarly, you may want to check that your power supply is installed in the appropriate operating conditions.
- The wiring of your unit should also be double-checked, in addition to its input voltage setting.
- Finally, you should also check for any electrical short that may have occurred.
- There also a number of tests that can be conducted with a multimeter to further drill down to the cause of your power supply’s failure.
Get a Quote
Request information for from Wall Industries.
"*" indicates required fields
Custom Solutions
Wall Industries, Inc. offers fully custom power design capabilities. Our team of electrical and mechanical power design engineers will utilize proven design topologies and concepts to create a solution to your power requirements. If you don’t have a specification, Wall’s engineering team will assist you in determining what your requirements are and how best to provide a solution.
Custom Power Supplies