Durability/Ruggedness (How a supply is designed for durability?)
Durability and ruggedness are probably the most important aspects of any military power supply. Durability ensures that a supply will last for a long time when facing the extreme environments often found in military applications. All design specifications are striving to ensure that you have a rugged power supply for your application. This can be achieved a number of ways depending on application and flexibility of the supply specifications.
Common challenges that call for ruggedization of a military supply include electrical reliability, shock and vibration, EMI, and environment. The supply will also need to be durable and reliable so it is sure to last for a long time in the field without damage.
Shock and Vibration
Shock and vibration are common in many military applications since they occur in almost any application that involves movement. Shock and vibration can be caused by factors such as acceleration, explosions, drops, or environmental factors like wind and lightning. There are very few military applications that are not threatened by some level of shock and vibration, which means that military supplies must be durable enough to withstand these types of environments. There are several ways to protect a supply from the effects of shock and vibration including changing the board layout, component staking, and encapsulation.
EMI
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMI) is a common occurrence in military applications. EMI can occur due to a number of factors like large current switches, environmental factors like lightening, interference from circuits, and noise from man-made or natural factors. EMI can severely interfere with how a power supply operates and could eventually lead to its failure. It is important that a military power supply is properly protected against EMI to ensure its longevity and reliability in the field.
EMI is common in military applications that have high vibration such as airplanes, helicopters, and ground vehicles. EMI in military applications can be reduced with a military grade EMI filter or shielding.

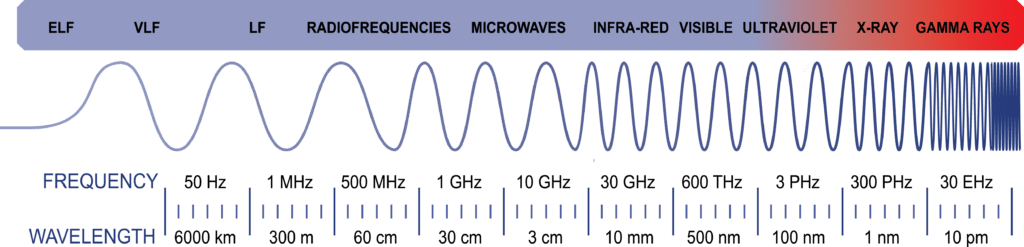
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Conducted Emissions
Conducted emissions consist of electromagnetic energy that is conducted back onto input cables. They can cause noise and distortion and can be problematic for other pieces of equipment in a system. High conducted emission levels can also cause problems throughout a whole power distribution network. There are certain conducted emission limitations of a supply depending on its application. For military power supplies, a filter can be used in order to meet the conducted emission limitations based on MIL-STD-461E.
MIL-STD-461E Conducted Emission Requirements
| Requirement |
Description |
| CE101 |
Conducted Emissions, Power Leads, 30Hz to 10kHz |
| CE102 |
Conducted Emissions, Power Leads, 10kHz to 10MHz |
| CE106 |
Conducted Emissions, Antenna Terminal, 10kHz to 40GHz |
Radiated Emissions
Radiated emissions are electromagnetic emissions which radiate out of a supply. These electromagnetic fields can interfere with electronic products that are nearby and can be harmful to those devices. To combat the release of radiated emissions in military power supplies, shielding can be used. Shielding requirements for military supplies are based on MIL-STD-461E.
MIL-STD-461E Radiated Emission Requirements
| Requirement |
Description |
| RE101 |
Radiated Emissions, Magnetic Field, 30Hz to 100kHz |
| RE102 |
Radiated Emissions, Electric Field, 10 kHz to 18 GHz |
| RE103 |
Radiated Emissions, Antenna Spurious and Harmonic Outputs, 10kHz to 40GHz |
EMI/RFI Susceptibility
Susceptibility of a military power supply refers to the tendency of a supply to break down due to exposure to unwanted emissions, or radio frequency interference. RFI can come from common electrical devices like switching power relays, laptops, and industrial controls, or environmental phenomenon like solar storms. This means that RFI is commonly found in many military applications like ship boards, planes, and helicopters. Each of these applications have their own RFI specs and limitations. To combat these emissions and meet the requirements of MIL-STD-461 (E), the supply can be hardened, the source of interference can be quieted, or the device can be shielded. A filter may also be used, but it should meet FCC and CE commercial compliance codes as well as military EMI emission codes.
MIL-STD-461E Susceptibility Requirements
| Requirement |
Description |
| CS101 |
Conducted Susceptibility, Power Leads, 30Hz to 150kHz |
| CS103 |
Conducted Susceptibility, Antenna Port, Intermodulation, 15kHz to 10GHz |
| CS104 |
Conducted Susceptibility, Antenna Port, Rejection of Undesired Signals, 30Hz to 20GHz |
| CS105 |
Conducted Susceptibility, Antenna Port, Rejection of Undesired Signals, 30Hz to 20GHz |
| CS109 |
Conducted Susceptibility, Structure Current, 60Hz to 100kHz |
| CS114 |
Conducted Susceptibility, Bulk Cable Injection, 10 kHz to 200 MHz |
| CS115 |
Conducted Susceptibility, Bulk Cable Injection, Impulse Excitation |
| CS116 |
Conducted Susceptibility, Damped Sinusoidal Transients, Cables and Power Leads, 10kHz to 100 MHz |
| RS101 |
Radiated Susceptibility, Magnetic Field, 30Hz to 100kHz |
| RS103 |
Radiated Susceptibility, Electric Field, 2MHz to 40GHz |
| RS105 |
Radiated Susceptibility, Transient Electromagnetic Field |
RFI
Radio frequency interference (RFI) can cause power supplies to breakdown unexpectedly. It is important that a supply is protected against this threat. Read more about RFI.
Environment (MIL-STD-810)
Military power supplies face incredibly harsh environments such as oceans, deserts, and high altitudes. In order for a power supply to withstand the effects of these extreme environments, it has to be properly ruggedized and tested. Mechanically and electrically, a supply can be ruggedized for environmental factors in a number of different ways including filtering, shielding, encapsulation, component staking, and hermeticity. Supplies should also be tested to MIL-STD-810 to ensure that it can withstand harsh military environments.
Altitude (Low Pressure)
Altitude is an issue for supplies that will be used in high altitude applications such as airplanes and rotary vehicles (helicopters). High altitude can cause gas or fluid leaks, physical and chemical property changes of low-density materials, material overheating, hermetic seal failure, and electrical material to malfunction or operate erratically. Testing a supply before it is used in high altitude applications is important to ensure that none of these consequences occur during operation.
Temperature
Low Temperature
If a product or material will be used in a low temperature environment during its lifetime, it needs to be properly tested to make sure it can withstand the effects of that environment. Low temperature environments can cause condensation, materials to harden and brittle, shock mounts to stiffen, and the performance of transformers and electromechanical components to change. Supplies must be designed to start and operate at the lowest design temperature and be able to withstand the effects of condensation at low temperatures. A supply can be protected against the effects of low temperature through conformal coating, encapsulation, or hermetic sealing.
High Temperature
A high temperature environment can be caused by a number of factors. Mobile environments like vehicles, planes, and ships, have higher temperature due to moving parts and limited space for heatsinking or cooling options. External environments like the desert will also have a higher temperature that will affect power supplies. High temperature environments can cause a number of issues for supplies including part binding, material dimensions changing, gaskets permanently setting, deterioration or closure of sealing strips, and lifetime shortening. These are just a few of the detrimental effects that a high temperature environment can have on a supply. The effects of high temperature can be combated through cooling methods like adding a heatsink or fan, utilizing moving air or liquid in the surrounding environment, or getting a custom supply to meet exact needs.

Water
Rain/Water Spray/Dripping Water
Any supply that will be exposed to rain, water spray, or dripping water during storage, transit, or operation, should be tested to ensure that they can withstand the effects of these environments. This will most commonly be a threat for airplanes, ships, and vehicles. When this type of water is in the atmosphere, it can interfere with radio communications, limit the effectiveness of radar, and even cause damage aircrafts during flight. On impact, rain, water spray, and dripping water can cause erosion to surfaces. After deposition or penetration, water can increase the potential of erosion, cause electrical material to malfunction, increase the weight of the supply, and modify thermal exchange. To protect a supply against rain, it can be hermetically sealed or conformally coated.
Immersion
Supplies that will be partially or completely immersed in water need to be properly tested to ensure that they will not be damaged by the effects of water. Effects can include corrosion due to direct exposure to water or high humidity levels, formation of electrically conductive paths that could cause malfunction, failure of engines to operate, or impairment of the burning quality of propellants and fuels. Products that will be immersed in water can be protected with a hermetic seal or conformal coating.
Humidity
Humidity is common in tropical latitudes year-round and mid-latitude areas seasonally. Humidity can have detrimental effects on a supply and materials including the oxidation or corrosion of metals, loss of strength, or delamination of composite materials. It is important that a supply is tested to standards in MIL-STD-810 to ensure it will not be damaged by humidity.
Sand and Dust
Supplies that will be exposed to blowing sand, blowing dust, or settling dust need to be properly protected from these elements. They can cause abrasion and erosion of surfaces, degradation of circuits, obstruction or clogging of openings or filters, and reduction of thermal conductivity. Supplies can be protected from sand and dust by a hermetic seal or conformal coating.
Altitude
High altitude environments, like airplanes or helicopters, can have a number of effects on supplies and materials being stored, transported, or operated at high altitudes. High altitudes can cause gas or fluid leaks, evaporation of lubricants, hermetic seal failure, erratic operation or malfunction of electrical material, physical and chemical property changes of low-density materials, and erratic starting and operation of engines.
Component Staking
Component staking is the process of applying an adhesive, like epoxy, to bond components to the PCB. This ensures that component leads will not be strained when they are exposed to shock and vibration. There are many different materials available to use for staking, and the best option will depend on the application and environment.
Component Mounting
Component mounting is the process of soldering components to a PCB so they do not move. All components must generally be soldered to help protect the component leads and joints from fracture. Component mounting can be very helpful in an environment affected by heavy shock and vibration.
Potting/Encapsulation
Potting/encapsulation involve the process of encasing either a portion of or an entire electronic assembly in a potting compound to protect the whole supply from shock, vibration and certain environmental factors. Materials like urethane, epoxy, and silicon rubber are typical for these methods. Before fully coating a supply, it is important to make sure the design can accommodate thermal expansion, the potting material is not too stiff or soft, and the material used is compatible with the components it is going to encounter. Any components that cannot be coated should be protected by a mask before the full product is coated.
Conformal coating is the process of covering a PCB in a thin coating. It generally protects a supply from moisture, dust, and condensation.
Hermeticity
Hermeticity is the process of making a power supply air tight and water tight. Hermeticity in a power supply typically involves sealing an entire component in an airtight case. This can be beneficial in protecting a military power supply from harmful environments where water, dust and sand, are a big threat. Supplies can be tested against MIL-STD-883 to ensure that they meet the military standards for hermetic sealing, fine and gross leak testing.
 Our NED series has an epoxy seal to protect it from the elements
Our NED series has an epoxy seal to protect it from the elements
Longevity/Derating
Derating a supply decreases output power below maximum capacity, while maintaining the supply’s current, voltage, temperature etc. Derating is a simple way to increase the longevity of the supply and ensure that components are not over-stressed. In a COTS military power supply, the derating levels will already be set and it could be costly to change them. Care should be taken not to derate a power supply to the point where power dissipation is increasing due to the efficiency curve of that particular power supply. Custom military supplies can be designed to operate at the most optimum point of your system.
Reliability/MTBF
Reliability is crucial for every military power supply. Reliability ensures that a supply can last for long times without failure. If a supply fails in the field, there could be drastic consequences. Reliability is typically higher in supplies that have simple designs, which is not always a possibility in a military spec power supply. When simplicity is not a viable option, reliability and MTBF can be improved through protection circuits, using high quality components, and preventative maintenance.
Military standards MIL-HDBK-217F calculate a failure rate of different electrical components like diodes, transistors, resistors and capacitors. The MTBF measurement depends on certain specifications like conditions of use, temperature, quality, design reliability, application, and environmental factors. These standards help set guidelines that ensure high reliability in military power supplies.
Military power supplies will also need to meet MIL-STD-810 which includes shock and vibration testing that the unit has to meet. Meeting these standards ensures that the supply can withstand the threat of shock and vibration and can last for long times in a harsh military environment.
A mil std power supply will be tested to certain standards to ensure that it is appropriate for any military application. These standards are very stringent to ensure that the supply will not fail when put up against harsh environments and applications.
MIL-STD-810: Environmental Testing
This standard covers environmental testing guidelines for military power supplies. This includes altitude, temperature, low temperature, high temperature, temperature shock, rain, immersion, humidity, contamination by fluids, fungus, icing/freezing rain, salt fog, sand and dust, vibration, shock, solar radiation (sunshine), acceleration, gunfire vibration, and ballistic shock.
MIL 461E: Electro Magnetic Emissions Requirements
This standard covers the requirements for the control of electromagnetic interference, both emission and susceptibility, for the electronic, electrical, and electromechanical equipment and sub systems for military applications for air, land, and sea.
MIL-STD-217: MTBF Standards
This standard outlines the way to estimate for inherent reliability in military equipment and systems. It also provides a common basis for comparing reliability for related or competitive designs.
MIL-STD-704: Aircraft Power Standards
More information on MIL-STD-704.
DO-160G
More information on DO-160G.
MIL-STD-1275: Military Vehicle Standards
More information on MIL-STD-1275.
MIL-STD-1399: Shipboard Standards
More information on MIL-STD-1399.
Air
Applications
Typical applications of the military air force are airplanes, satellites, and helicopters.
Environmental Conditions/Challenges
Supplies that will be used in military air applications have to be tested to withstand high altitude, high temperature, low temperature, and rain/water environmental factors.
Typical Design Requirements
Due to the extreme environment they are used in, military supplies used in air applications will typically have to be designed to withstand extreme EMI, RFI, and shock and vibrations.
Safety/Mil Specs
DO-160G
This standard specifically covers environmental conditions and test procedures for airborne electrical and electronic equipment.
MIL-STD-704: Aircraft Power Standards
This standard ensures compatibility between aircraft electric system, external power, and airborne utilization equipment.
Land
Applications
Typical military applications on land include ground vehicles, armored vehicles, and amphibious vehicles.
Environmental Conditions/Challenges
Supplies used in military applications on land should be tested to withstand high temperature, low temperature, rain/water, and sand and dust.
Typical Design Requirements
Typically, in land based military applications, space is at a premium and supplies need to be as compact as possible. Supplies in vehicle applications will also face the risk of shock and vibration.
Safety/Mil Specs
MIL-STD-1275: Military Vehicle Standards
This standard covers the limits of transient voltage characteristics and steady state limits of 28VDC electrical power circuits in military vehicles.
Sea
Applications
Typical military applications on the sea include ships, submarines, and amphibious vehicles.
Environmental Conditions/Challenges
Supplies used in military applications on the sea should be tested to withstand water, high temperature, and low temperature conditions.
Typical Design Requirements
Due to the extreme environment they are used in, military supplies used in applications on the sea will typically have to be designed to withstand extreme shock and vibrations and RFI.
Safety/Mil Specs
MIL-STD-1399: Shipboard Standards
This standard covers the standard interface requirements for the constraints on the design of shipboard user equipment that will utilize shipboard AC electric power.














 Applications like military helicopters have needed to adapt to new technologies.
Applications like military helicopters have needed to adapt to new technologies.