Non-Isolated DC DC Converters
Our non-isolated regulators offer efficient and reliable voltage regulation for a wide range of industries, including automotive, industrial automation, telecommunications, and more.
With a focus on performance, flexibility, and space-saving designs, our regulators provide precise voltage regulation, advanced control features, and robust protection mechanisms to ensure stable and consistent power output. Whether you require step-down or step-up regulators, adjustable voltage regulators, buck-boost, or point-of-load our product lineup offers a variety of options to suit your specific requirements.
Explore our collection of non-isolated regulators to find the ideal power regulation solution that empowers your systems with enhanced performance and reliability.
| Series | Input Range |
Input Voltage |
Output Voltage |
No. Outputs |
Output Power (W) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
DCMAR1 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 6.5~32, 15~32 | Input Voltage: 6.5~32, 15~32 | Output Voltage: 3.3, 5, 12 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): - | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The DCMAR1 series of DC/DC switching regulators offers 1A of output current in a compact industrial 0.45” x 0.30” x 0.40” standard SIP-3 package. | ||||||
DCDA1 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 4.75~36, 6.5~36, 9~36, 12~36, 15~36, 18~36 | Input Voltage: 4.75~36, 6.5~36, 9~36, 12~36, 15~36, 18~36 | Output Voltage: 1.8, 2.5, 3.3, 5, 6.5, 9, 12, 15 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): - | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The DCDA1 series of non-isolated DC/DC converters offers 2A of output current in an ultra-compact 0.45” x 0.33” x 0.69” 3-Pin SIP package. | ||||||
DCNSR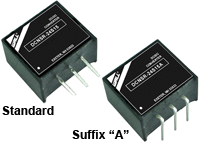 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 10.5-36, 13.5-36, 16.5-36, 4.6-31, 4.6-32, 4.6-36, 6.5-36, 7-21, 7-24, 7-27, 7-29, 8-36 | Input Voltage: 12/24 | Output Voltage: 1.2, 1.5, 1.8, 2.5, 3.0, 3.3, 5, 6.5, 9, 12, 15 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 1.2, 1.5, 1.8, 2.5, 3, 3.3, 5, 6.5, 9, 12, 15 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The DCNSR series consists of high performance non-isolated DC/DC converters that deliver 1A of output current in a 0.46” x 0.40” x 0.30” 3-Pin SIP package. This series has an operating temp of -40~85°C, up to 95.5% efficiency, and short circuit protection | ||||||
DI01D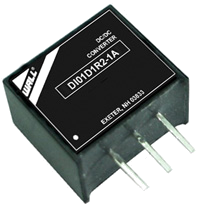 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 12-36, 15-36, 18-36, 4.6-36, 4.75-36, 6.5-36, 9-36 | Input Voltage: 9, 12, 24 | Output Voltage: 1.2, 1.5, 1.8, 2.5, 3.3, 5, 6.5, 9, 12, 15 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 1.2, 1.5, 1.8, 2.5, 3.3, 5, 6.5, 9, 12, 15 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The DI01D series consists of high performance non-isolated DC/DC converters that deliver 1A of output current in a 0.45” x 0.40” x 0.30” 3-Pin SIP package. This series has an operating temp of -40~85°C, up to 96% efficiency and short circuit protection. | ||||||
CV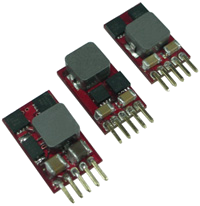 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 10~30, 2.5~5.5, 4.5~14 | Input Voltage: 5, 12, 24 | Output Voltage: 0.6~3.3, 0.59~6, 3~6, 5~15 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 1.8~9.9, 1.77~18, 9~18, 15~45 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
DC DC Converters - The CV series consists of non-isolated DC/DC converters that deliver up to 3A of output current in a small open frame package. This series has both positive and negative output applications. | ||||||
POL06-05T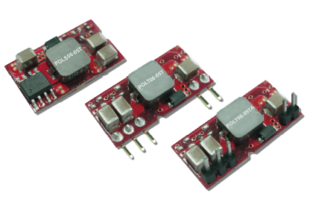 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 2.4~5.5 | Input Voltage: 5 | Output Voltage: 0.75~3.3 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 4.5~19.8 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The POL05-05T series of DC DC open frame converters delivers up to 6A of output current in a small size and low profile package. | ||||||
POL06-12T Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 8.3~13.2, 8.3~14 | Input Voltage: 12 | Output Voltage: 0.75~5 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 4.5~30 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The POL06-12T series of DC DC open frame converters offers up to 6A of output current. | ||||||
DCPSD12 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 11~15 | Input Voltage: 11~15 | Output Voltage: 5~6, 6~8, 8~10, 13~16, 16~21, 21~27, 27~33, 33~48 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 5, 6, 8 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The DCPSD12 series of non-isolated DC/DC supplies offers up to 8 watts of output power in a 3.52in x 1.51in x 1.20in compact package. | ||||||
POL10-05T Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 2.5~5.5 | Input Voltage: 5 | Output Voltage: 0.75~3.3 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 7.5~33 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The POL10-05T series of DC/DC open frame power converters offers 10A output current rating in a small size and low profile package. | ||||||
POL10-12T Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 8.3~13.2, 8.3~14 | Input Voltage: 12 | Output Voltage: 0.75~5 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 7.5~50 | Get a QuoteDownload Datasheet |
The POL10-12T series of DC/DC open frame power supplies offers a 10A output current rating in a small size and low profile package. | ||||||
What is a non-isolated DC DC converter?
A non-isolated DC DC converter forgoes using a transformer to eliminate the DC path between its input and output. Integrated circuits (ICs) typically serve the same purpose that a transformer would.
When would you use a non-isolated power supply?
Non-isolated power supplies are often used in LED-lighting, appliances and sensor applications.
What is the difference between isolated and non-isolated?
Non-isolated DC DC converters use a single circuit, allowing current to flow from input to output. Isolated DC DC converters, meanwhile, prevent DC current flow between input and output by separating the circuit into two sections.
Do I need a non-isolated DC-DC converter for my industrial application?
Isolation is typically required in an applicaton for safety reasons. If an application doesn’t require isolation, non-isolated converters are available to power equipment, offering a compact size, improved efficiency and cost savings.
What is the main difference between isolated and non-isolated converters?
For isolated DC-DC converters, there is separate ground between input and output stages, which provides enhanced safety when exposed, wheres a non-isolated converter allows direct current flow between the two sides as they share a common ground.
What are the main benefits of using a non-isolated converter?
Non isolated converters utilize fewer components, making them more compact and a lower cost alternative to isolated converters. Furthermore, non-isolated converters typically provide higher efficiency which provides cost-savings over time.
What should I consider when choosing a non isolated converter?
After determining proper input and output specifications, it is also important to consider efficiency, power loss, and electrical noise generated by the converter in order to ensure you are using the proper non-isolated converter for your application.
Get a Quote
Request information for from Wall Industries.
"*" indicates required fields
Custom Solutions
Wall Industries, Inc. offers fully custom power design capabilities. Our team of electrical and mechanical power design engineers will utilize proven design topologies and concepts to create a solution to your power requirements. If you don’t have a specification, Wall’s engineering team will assist you in determining what your requirements are and how best to provide a solution.
Custom Power Supplies