PSAYC Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 90~305 | Input Voltage: 115/230 | Output Voltage: 3.3, 5, 9, 12, 15, 24 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 2 | Get a QuoteDownload
Datasheet |
AC DC Power Supplies - The PSAYC series of AC DC power supplies provides 2 Watts of output power in an encapsulated PCB mountable package. This series consists of single output models with a 90-305VAC (120-430VDC) input voltage range.
|
PSAZC Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 90~305 | Input Voltage: 115/230 | Output Voltage: 3.3, 5, 9, 12, 15, 24 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 2 | Get a QuoteDownload
Datasheet |
AC DC Power Supplies - The PSAZC series of AC DC power supplies provides 2 Watts of output power in an encapsulated PCB mountable package. This series consists of single output models with a 90-305VAC (120-430VDC) input voltage range.
|
IGBT2 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 10.8-13.2, 13.5-16.5, 21.6-26.4 | Input Voltage: 12, 15, 24 | Output Voltage: -15, -9, -5, -3.5, -3, 15, 17, 18, 20 | No. Outputs: D | Output Power (W): 2 | Get a QuoteDownload
Datasheet |
The IGBT2 series of IGBT SiC gate drivers offers 2 watts of output power in an industry standard 0.77” x 0.39” x 0.49” SIP-7 package.
|
PSAIC Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 90~264 | Input Voltage: 115/230 | Output Voltage: 3.3, 5, 9, 12, 15, 24 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 2.97, 3 | Get a QuoteDownload
Datasheet |
AC DC Power Supplies - The PSAIC series of AC DC switching power supplies offers 3W of output power in an encapsulated PCB mountable package. This series consists of single output models with a 90-264VAC (120-370VDC) input voltage range.
|
PSFAA-03 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 85~264 | Input Voltage: 115/230 | Output Voltage: 3.3, 5, 9, 12, 15, 24 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 3 | Get a QuoteDownload
Datasheet |
The PSFAA-03 series of AC/DC power modules offers up to 3 watts of output power in a fully encapsulated 1” x 1” x 0.64” plastic case.
|
PSAOC Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 90~264 | Input Voltage: 115/230 | Output Voltage: 3.3, 5, 8, 9, 12, 14, 15, 24 | No. Outputs: S, D | Output Power (W): 3.5, 3.6, 3.96, 4 | Get a QuoteDownload
Datasheet |
AC DC Power Supplies - The PSAOC series of AC DC power supplies provides 4 Watts of output power in an encapsulated PCB mountable package. This series consists of single output models with a 90-264VAC (120-370VDC) input voltage range.
|
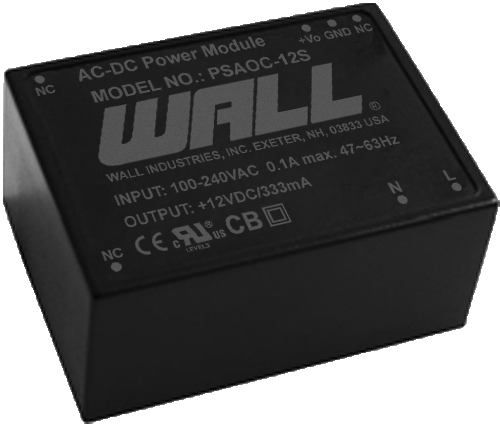
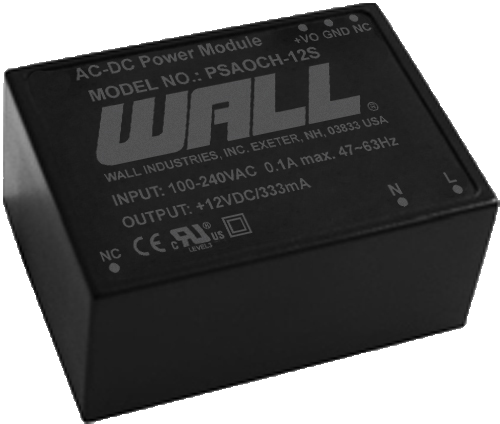
PSAOCH Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 90~305 | Input Voltage: 115/230 | Output Voltage: 3.3, 5, 8, 9, 12, 14, 15, 24 | No. Outputs: S, D | Output Power (W): 3.5, 3.6, 3.96, 4 | Get a QuoteDownload
Datasheet |
AC DC Power Supplies - The PSAOCH series of AC DC switching power supplies offers 4W of output power in an encapsulated PCB mountable package. This series has single and dual output models available with a 90-305VAC (120-430VDC) input voltage range.
|
PSAHC Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 90~264 | Input Voltage: 115/230 | Output Voltage: 3.3, 5, 12, 15, 24 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 4, 5, 5.5 | Get a QuoteDownload
Datasheet |
AC DC Power Supplies - The PSAHC series of AC DC power supplies offers 5 Watts of output power in an encapsulated PCB mountable package. This series consists of single and dual output models with a 90-264VAC (120-370VDC) input voltage range.
|
DCPDL06 Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 18~36, 36~75, 4.5~9, 9~18 | Input Voltage: 5, 12, 24, 48 | Output Voltage: 3.3, 5, 9, 12, 15, 24, ±5, ±12, ±15 | No. Outputs: S, D | Output Power (W): 4.3, 6 | Get a QuoteDownload
Datasheet |
DC DC Converters - The DCPDL06 series of DC DC power converters provides 6 Watts of output power in a small SIP package. This series has single and dual output models with 2:1 input voltage ranges. Models are RoHS compliant and have UL60950-1 approvals.
|
POL06-05T Series Description: The PSAYC series of AC/DC switching power supplies provides 2 watts of output power in a 1.33" x 0.87* x 0.67* encapsulated PCB mountable package. | Input Voltage: 2.4~5.5 | Input Voltage: 5 | Output Voltage: 0.75~3.3 | No. Outputs: S | Output Power (W): 4.5~19.8 | Get a QuoteDownload
Datasheet |
The POL05-05T series of DC DC open frame converters delivers up to 6A of output current in a small size and low profile package.
|
What are industrial power supplies?
Industrial power supplies are electrical devices used to provide power to industrial machinery. Any device that provides electrical power to a circuit can be deemed a power supply. In some cases, a power supply may be used to provide power to different electrical loads. The three most commonly used types of industrial power supply are switching power supplies, unregulated power supplies and linear power supplies.
Whilst unregulated power supplies are the simplest to construct and tend to be of rugged build, they are not best suited for industrial settings as they do not produce a clean voltage. As the supply is unregulated, any change occurring in input voltage will be reflected on the output voltage. These changes amount to electrical noise, known as ‘ripple voltage’. When power supply and load requirements are closely matched, this can be kept to a minimum, but if the ripple voltage is large enough, it can negatively impact circuits and devices connected to it.
Linear power supplies were once the favored choice for industrial applications. A linear regulated power supply provides a constant output voltage, which is independent of the output current. They are often promoted as a clean DC voltage source, whilst also having very low output voltage ripple and noise. These power supplies are still useful when the application requires a large inrush current. However, over time this form of industrial power supply has been outmatched in size, weight and efficiency by switching power supplies.
Switching power supplies are the most widely used in industry today. They are smaller, more efficient devices that convert the AC input voltage into low voltage DC. These power supplies can be 25% more efficient than their linear supply counterparts, whilst also being 25% the size of the older devices. These advantages have made switching power supplies the best choice for most industrial applications today. However, it’s important that the requirements of the application must be understood before one is chosen.
How to choose an industrial power supply?
Choosing an industrial power supply requires an assessment of the requirements of each device that it will be connected to. Reviewing the specifications of the devices that will be drawing power from the supply helps to ascertain the correct type of supply needed. For example, some devices may require a very clean output, and although linear power supplies tend to be less noisy on the output than switching power supplies, they can be just as quiet if designed with output noise in mind.
Regardless of the type of industrial power supply that is chosen, it’s still necessary to ascertain the DC input requirements of each device and calculate how much power each device will be drawing from the supply so that it can prove sufficient to the task. In the case of switching power supplies, the output voltage is generally adjustable. Modern power supplies are fitted with sensors to determine what voltage to apply, as well as over-voltage protectors – however, under-voltage can then another problem to contend with.
Power requirements should be carefully considered before any decision is made. Each device has its own unique set of requirements and whilst smaller components (such as solenoids and indicators lights) may seem small enough to dismiss, when compounded on a large scale these can have a real impact on overall requirements. A common rule of thumb is to calculate power requirements as accurately as possible and then add an extra 25%, in order to ensure spare capacity and guaranteed performance.
How are industrial power supplies designed for industrial applications?
Power supplies designed for industrial applications will be able to withstand harsh environments and high temperatures. Industrial power supplies will typically be compact and will also perform well in terms of efficiency, permissible operating temperature, bridging time in the event of a power failure and thermal management.
Quality industrial power supplies will have heat management systems in place which allows the supply to be installed in any direction. This will allow the power supply to provide constant performance, even at high temperatures. Low-quality power supplies will lack the protective mechanisms required to automatically throttle the power output back when necessary.
What are the features and parameters of an industrial power supply?
Features and parameters to consider when choosing an industrial power supply are:
- Rated power: The amount of power that the supply can deliver in continuous operation. This should meet the requirements of your application.
- High efficiency: Industrial power supplies are designed to have particularly high efficiency, which reduces operating costs in the long term.
- Low Operating costs: High efficiency leads to low power dissipation and less heat generation. This reduces the load on individual components and increases the lifespan and lowering operating costs.
- Input voltage derating: This indicates which power can be taken at which input voltage.
- Good temperature behavior: Industrial power supplies should be able to perform consistently at high temperatures.
- Low weight: A light power supply is particularly important for mobile industrial applications.
- Mounting position: Shows which alignments of the power supply unit are permissible in order to reliably dissipate the heat loss.
- Safety: Protection against short-circuit, overload, overvoltage and overheating. This includes proper agency approvals.
- Electromagnetic compatibility: Electrical devices must not interfere with each other.
How reliable are industrial power supplies?
The mean time between failure (MTBF) is one way that a power supply’s reliability can be measured. This measurement takes into account the middle section of a power supply’s lifespan, and therefore does not take into consideration ‘infant mortality’ or wear and tear, that may impact a power supply towards the end of its lifespan.
A MTBF is determined according to various standards such as MIL HDBK 217F, Bellcore/Telcordia TR-332 or SN29500, sometimes known as the ‘Siemens standard’. As each standard varies in its calculation methods, comparisons of MTBF values should only be made between values measure under the same standard and testing conditions.
MTBF of switched-mode power supplies is calculated from the sum of the values of each component. This means that the power supply’s ‘component count’ will have a direct impact on its MTBF. Whilst switched-mode power supplies tend to have higher MTBF values as a result, this does not necessarily correspond to better reliability. MTBF offers a valuable point of comparison when assessing reliability between similar devices, but it does not give you an estimated lifespan. This is only possible through extensive testing.
How are industrial power supplies tested?
Industrial power supplies are tested for performance and reliability in a number of ways. A highly accelerated stress test (HAST) conducted over a 96-hour period is one method to produce an estimated lifespan for an industrial power supply. In a HAST, a device is placed in a climactic chamber that is set to extreme conditions (high humidity, temperature, and vibration) as a storage test. The device is not in operation whilst in the chamber.
The power supply’s performance is then tested and compared to its datasheet parameters before undergoing the HAST. The difference in values between performance before and after the HAST can be used to calculate overall service life. The results of this test can then be verified with a 1000-hour storage test or a life test, where the device is tested in operation at the maximum permissible ambient temperature.
Who can design your industrial power supply? Why is Wall the best choice?
As an industrial power supplier, Wall Industries is here to ensure the highest quality supply for any industrial application. We have standard wall mount, desktop, open frame, chassis mount, DIN rail, enclosed, and LED industrial grade power supplies if AC/DC is needed, as well as surface mount and through hole options for DC/DC. We also offer extensive custom capabilities and have many years of experience designing highly efficient power sources that meet any industrial specifications. Explore our solutions or get in touch with us today.