Selecting the right power supply for military applications involves considering whether a design meets industry requirements. Among these is the MIL-STD-1275, which sets out the expected characteristics of 28VDC power supplies for use in military ground vehicles.
The MIL-STD-1275 is a widely utilized standard for assessing power supplies for use in ground vehicle applications. As you would expect, power supply solutions that comply with the standard must be able to withstand harsh conditions and environmental challenges.
The goal of this standard is to ensure that application systems in military ground vehicles receive reliable power through efficient and robust power supply solutions.
In this post you’ll find an in-depth guide to the requirements of the MIL-STD-1275 and what to look for in quality power supply solutions. Analysis will also include the evolution of the standard over time, additional supplementary standards, and advice for navigating the requirements.
What is MIL-STD-1275?
MIL-STD-1275 is a military standard concerning the characteristics of 28V Direct Current input power solutions for utilizing the equipment in ground-based military vehicles. Utilization equipment for this application includes electronic devices, systems, and equipment.
The MIL-STD-1275 is the standard used by the Department of Defense (DOD) and all associated departments and agencies.
As stated in the official document – ‘The intent of this document is to describe the nominal 28 VDC voltage characteristics, common across military ground vehicles, at the input power terminal of the utilizing electrical and electronic assemblies directly connected to the distribution network.
This lays the groundwork for commonality across vehicle platforms. The vehicle’s design authority is responsible to ensure that the 28 VDC delivered to the input power terminal of the utilization equipment meets these requirements.’

Key features of ruggedized power supplies for military applications
Military power supplies must function effectively to support a variety of different systems, while remaining reliable in extreme conditions. Ruggedized military power supply solutions can be categorized by:
- Protection against voltage spikes – converters and power supplies should be able to accommodate a wide range of input voltages. This helps account for sudden large changes in voltage. For reference, our high voltage input solutions have an input voltage range of 18-750 VDC.
- Resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI) – radio frequency interference (RFI) and electromagnetic interference can cause electronic components to fail or degrade in performance.
- Wide range of operating temperatures – military power supplies, and any power solution designed for use in extreme conditions, should be able to withstand temperatures from below -40°C to above 80°C. At Wall Industries, operating temperatures can meet -55°C to +125°C where requested.
- Shock and vibration resistance – military vehicles must often traverse difficult terrain, leading to significant vibrations and shocks. It’s important that power supplies are resistant to this, as it can cause wiring faults and other forms of damage to internal components.
- Noise reduction – tactical considerations often require electronic systems to operate at low ripple and noise.
How MIL-STD-1275 has changed over time
The background to the current version of the standard follows a history of revisions, each expanding it in scope and detail to improve compatibility between military vehicle power supplies and their end systems.
Established requirements for power supplies to deal with voltage spikes, energy surges, steady-state conditions, and voltage ripples. At the time, it was left to the procuring authority to define how equipment should operate during and after such disturbances.
Requirements were updated to include limits for fault conditions to be evaluated. Here, 14Vdc component requirements were established in line with the limits placed on 28V components.
The main difference brought about by revision C of the standard was the expansion of the required temperature range for compliance. Previously, vehicle power systems were required to operate within -32°C to +52°C, which was increased to -45°C to +82°C. It was at this time that several references to SAE standards dealing with EMC were added to supplement the already-accepted MIL-STD-461 requirements.
The changes brought about to the standard at this time reinstated the -32°C to +52°C temperature range for evaluating products. In addition, there was an exemption of CE102 compliance for conducted emission compliance of the power system..
Introduced an ambient temperature for testing purposes of +23°C (± 5°C). Extreme temperature evaluations were provided by the standard as deemed fit by the approving authority.
- 2022: MIL-STD-1275 F (The current version of the standard at the time of writing)
; This version introduced many overhauls and improvements on the previous revision. Of these, a major change is the addition of the new 500-ms load-dump pulse requirement, which is more severe than what was included in the previous revision. This is important to account for positive voltage surges resulting from an alternator load dump. Excess surge energy can damage or destroy the electrical system in military land vehicles unless components are suitably ruggedized.
Power supply standards outlined in MIL-STD-1275
The MIL-STD-1275 standards define a series of test conditions designed to instill 28V electrical power systems with an immunity to various factors when used in military vehicles. As mentioned before, the primary focus of the standard is to ensure the functionality of equipment connected to 28V distributions systems inside military vehicles.
Voltage compatibility requirements
The standard dictates that the steady state operation for equipment under test (EUT) is between 20 and 33 VDC. Deviation from normal operation at either extreme is considered a failure. This testing includes voltage ripples. Here, the EUT is subjected to a ripple voltage up to 2V above and below its steady state amount. The resulting emitted voltage should then not exceed 1V above or below the steady state voltage.
It’s generally accepted that the duration of voltage compatibility testing should last as long as it takes for the EUT to reach thermal stability at each current extreme. This is defined as the EUT achieving a temperature variation of <1°C for three consecutive measurements, each with 15 minute intervals.
It’s also important to note that the MIL-STD-1275 standard recommends the use of 5 µH LISNs (Line Impedance Stabilization Networks), which may not be compatible with some of the other military standards testing we’ll be discussing later on.
Starting and transient disturbance requirements
The standard states that equipment must operate without damage or degradation when being subjected to disturbances associated with engine starts. Common examples include Initial Engagement Surges (IESs) and cranking surges. Some converters must operate through these cranking disturbances. Wall Industries offers multiple custom converters with this function.
On top of this, the MIL-STD-1275 provides an acceptable circuit to perform injected voltage spikes tests. The rise time should not exceed 50 nanoseconds (ns) with a frequency of oscillation above 20 kHz and less than 500 kHz. Regarding voltage surges, utilization equipment should not emit surges above:
- 100V for 50ms – down to 33V for 500ms
- 18V for 500ms up to 20V for 600ms
Figure 1 (EMC Directory) 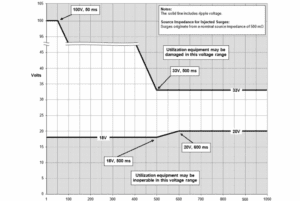
For voltage spikes, utilization equipment should operate without degradation or damage in the presence of the below-mentioned injected voltage spike levels and not emit spikes over these levels:
- +250V for 70µs – down to 100V for 1ms (figure 2)
- -250V for 70µs up to 18V for 1ms
Figure 2(EMC Directory)
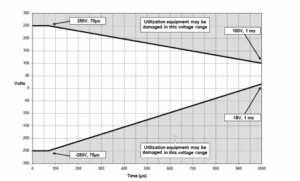
Reverse polarity requirements
To test the reverse polarity current for the standard, the EUT should be given a 33V DC power supply with the power leads reversed for 5 minutes. The reverse polarity current must not exceed the normal operating current for the EUT to be considered a success. This is then validated by testing the EUT by supplying the correct polarity, with any deviation from the normal operating current being considered a failure for the MIL-STD-1275.
Benefits of the MIL-STD-1275F standard
You should always look for power supplies that have passed this standard to secure a robust solution for your needs. The benefits when used for military vehicle systems include:
- Reverse polarity protection
- Ability to operate efficiently with a steady state input voltage of 20V to 33V
- Operation during initial engagement and cranking surges resulting from vehicle start-up
- Supply that will tolerate injected spikes and surges without emitting a resultant spike or surge greater than what’s permitted by the standard
- Resistance to challenging conditions and high performance when used in highly demanding applications
- Management and resistance to EMI/RFI
Oftentimes, the best way to guarantee compliance with the MIL-STD-1275 standard is to employ a proven input protection module. When implemented in power supplies and DC DC converters, this module ensures safe operation of the power supply by protecting it from overvoltage, inrush currents, and reverse voltage.
A note on Data Item Descriptions (DIDs)
For the purposes of documenting testing and evaluation, MIL-STD-1275 does not specify a DID. However, the DID structure associated with the MIL-STD-461 provides an appropriate report outline which can be adapted for MIL-STD-1275 use. The only caveat is that it should be clear which sections relate specifically to MIL-STD-1275 to avoid confusion on the part of the approving authority.
EMC and ESD requirements
Although not covered by the MIL-STD-1275 standard, the EUT must comply with military standards for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and electrostatic discharge (ESD) prior to testing systems and products for the MIL-STD-1275 standard. These compliance requirements we’ll cover in detail below when discussing the MIL-STD-461 standard.
Environmental testing conditions
When testing utilization equipment for MIL-STD-1275F compliance, environmental conditions should be the following:
- Temperature: 23°C ± 5°C
- Relative humidity: Between 0% and 90% humidity
- Atmospheric pressure: 80kPa to 102kPa
Note that these requirements, although accurate at the time of writing, could change over time with the introduction of subsequent revisions to the standard.
Other Military standards for power supplies
Depending on the exact nature of your military application, there will be additional standards that you should look for when selecting a power supply solution. Some of these include:
Mil-Std-461 – Electro Magnetic Emissions Requirements
This standard outlines requirements on military products ‘for the control of electromagnetic interference characteristics of subsystems and equipment’. The intention is to make sure systems are ruggedized so they can function effectively in electromagnetic environments (EM) and avoid causing electromagnetic interference (EMI) to nearby devices. This is important, as energy on the electromagnetic spectrum can disrupt systems, causing a decline in the performance of key systems or a system shut down.
Electromagnetic compatibility testing considers a device’s susceptibility to both conducted and radiated EM emissions. This typically applies to devices which have “electronic enclosures that are no larger than an equipment rack, electrical interconnections that are discrete wiring harnesses between enclosures, and electrical power input derived from prime power sources”.
Mil-Std-202 – Standardized Test Methods
This Department of Defense document sets out uniform methods for testing electronic and electrical component parts. As such, the MIL-STD-202 must be referred to frequently when testing products for use in military settings. The primary goal of the standard is to assess components for environmental resistance before they are deployed. As a result, the standard includes basic environmental tests. The general requirements of the MIL-STD-202 standard include:
- Required tests
- Testing conditions
- Permissible temperature variation in environmental chambers
- Reference conditions
- Calibration requirements
Mil-Std-810 – Environmental Testing
Aims to determine whether a product can withstand the effects of harsh environmental conditions. This military standard is widely recognized, with many commercial manufacturers testing their products for ruggedness using the MIL-STD-810 H. The standard includes test methods for mechanical vibrations, high & low temperatures, humidity, shock, low pressure, and more. Alongside these tests for common environmental conditions, the standard also outlines test methods for environmental factors that are specific to military vehicles, such as MIL-STD-810 H Test Method 519.8 Gunfire.
MIL-HDBK-217 – Reliability Prediction
This standard establishes failure prediction models for various types of electronic military equipment. This reliability prediction standard contains testing requirements for analyzing the mean time between failures (MTBF) of electronic equipment, with the goal of improving the reliability of military systems. This applies to resistors, capacitors, logic arrays, microprocessors, gate arrays, and digital and linear microcircuits.
Mil-Std-704 – Aircraft Power Standards
The MIL-STD-704 lays out standards for safe and reliable aircraft electrical systems and associated power supplies. AC power requirements specify the transient voltage characteristics and operating voltage limits are both measured within 10cm of the utilization power input terminals.

Concerning external power sources, these follow the same guidelines, with an increased lower voltage limit to account for longer wiring. Required voltage for external power supplies is still measured at the terminals for utilization equipment.
DC power requirements follow the same 10cm measurement distance as AC power supplies, starting from the EUT power connector. The table below contains the test matrix for DC power requirements.
Mil-Std-1399 – Shipboard Standards
Being approved by the Naval Sea Systems Command, the MIL-STD-1399 is available for use by all Department of Defense Agencies and Departments. Its purpose is to ensure onboard user equipment utilizes ship AC electric power through the defining of standard interface requirements and applicable constraints. The types of shipboard electric power to be supplied are specified by MIL-STD-1399 as follows:
- Type I: The standard shipboard electric power source should provide 440 or 115 volts (V), 60 hertz (Hz) ungrounded. Type I power shall be used unless a deviation is granted.
- Type II: This power is 440 or 115 V, 400 Hz ungrounded and has only limited application. Use of type II power requires the submittal and approval of a deviation request.
- Type III: Type III power is 440 or 115 V, 400 Hz ungrounded, having tighter tolerances as compared to types I and II. Type III power has restricted use and deviation request submittal and approval is required before it can be used.
Custom power supplies for commercial and military applications
The requirements for military power supplies under MIL-STD-1275 are in place to test systems used in vehicles. While it might seem like a lot to consider, this standard should be viewed as supplementary to others for military vehicle systems, such as MIL-STD-461. When implemented together, Mil standards ensure your power supplies are ruggedized for a variety of extreme environments and conditions.
We understand it’s imperative that power supplies for military vehicles to function effectively in high-risk conditions where performance cannot be compromised. Standards such as the MIL-STD-1275 have been developed over years of lab and field testing to ensure the safety of military personnel through the expected operation of utilization systems.
Our team of expert engineers can design you a custom military power solution that’s compliant with all relevant military application standards, and delivers exceptional performance. We also have a wide range of leading market products intended for military use. Get in touch to discuss how we can help.
